Science
BENGALURU: IISc team finds way to block a superbug transporter
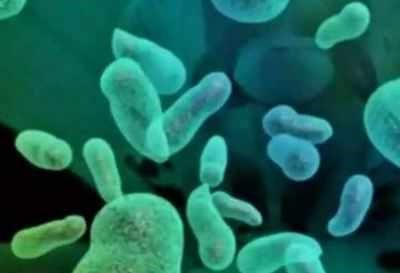
BENGALURU: Researchers from the Indian
Institute of Science’s (IISc) Molecular Biophysics Unit (MBU) have found a
novel way to block bacteria from flushing out antibiotics which helps them gain
drug resistance.
The new finding holds the potential of making existing drugs more effective
against drug resistant bacteria or superbugs.
What they’ve essentially done is use a specific antibody found in Indian camels
(at the National Research Centre on Camel, Bikaner) to block a transporter that
helps bacteria flush out drugs. At present, the team, led by Aravind Penmatsa,
assistant professor at MBU, has demonstrated the finding in laboratory
conditions.
Bacteria are generally killed by the use of antibiotics. One of the mechanisms
they use to gain resistance is called efflux — the process in which bacteria
transport compounds such as drugs outside the cell — and transporters play a
crucial role in enabling the pathogen to perform this.
That transporters are among major
components in the multidrug resistance armoury of bacteria, understanding the
molecular architecture of these cell membrane-embedded machines paves the way
for designing inhibitors against them, thereby helping in the treatment of
diseases caused by these bacteria.
And, according to IISc, in a new study, the researchers “have solved the
atomic-resolution structure of one such transporter, NorC, in complex with an
Indian camelid antibody (ICab).”
Though transporters are molecular machines that need to shift their
conformation (shape/structure) to transport substrates, the team found that the
binding of ICab to NorC locked it into a single conformation.
Not only did the transporter get locked in a single state, but the ICab
effectively plugged the transporter like a “bottle-cork”, rendering it
incapable of interacting with antibacterial compounds (drugs), the researchers
said.
“…The process of efflux is very important for bacteria and one of the major strategies that hasn’t yet been explored as a therapeutic mechanism is to develop molecules that can block efflux. If we are able to block transporters that help efflux of certain antibiotics, those drugs will gain efficacy. In some sense, we can enhance the efficacy of available antibiotics if we have blockers of efflux and that’s the potential medical benefit of what we’ve found,” Penmatsa told TOI.
NorC is a transporter found in Staphylococcus aureus — a type of bacteria often found on the skin and in the upper respiratory tract of humans — that helps provide resistance against broad-spectrum antibiotics like norfloxacin and moxifloxacin.
“These insights will significantly help formulate strategies to counter
transporter-mediated antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria, using tools
like camelid antibodies. The structure of NorC and the conformation it has been
solved in is also the first-of-its-kind, providing a model to study similar
drug efflux transporters from other pathogenic bacteria,” IISc added.
The study was primarily funded by the DBT-Wellcome Trust India Alliance and the department of biotechnology.
Science
SAN FRANCISCO: Indian-Origin Founder Unveils Wearable Device That Records Every Moment Of Your Life

SAN FRANCISCO: Advait Paliwal, an Indian-origin entrepreneur, has recently introduced a wearable AI device called Iris, designed to provide users with “infinite memory.” According to Paliwal, the device captures “pictures every minute,” which are stored either on the device or in the cloud, allowing users to preserve life’s small moments and recognize patterns often overlooked.
In a series of tweets, Mr Paliwal, who is based in San Francisco, explained that Iris not only organises the photos into a timeline but also uses AI to generate captions and help users recall forgotten details. Additionally, the device features a “focus mode,” which detects when the wearer is distracted and offers reminders to refocus.
Mr. Paliwal shared that the design of Iris is inspired by the evil eye symbol. He developed the device over the summer at the Augmentation Lab in Cambridge, part of a two-month AI and hardware talent accelerator program. After the program, Mr Paliwal presented Iris to over 250 attendees at the MIT Media Lab, where he received positive feedback, with many expressing interest in owning the device.
Highlighting its potential, Mr Paliwal suggested that Iris could offer safety and health benefits, such as aiding doctors in understanding patients’ daily habits or ensuring workplace safety compliance. In elderly care, the device could help caregivers monitor patients without being intrusive.
However, after Mr Paliwal shared his post on X (formerly Twitter), reactions were mixed. While some users expressed excitement, others raised privacy concerns. One person commented, “It’s an interesting concept, but I wouldn’t want to interact with someone wearing this, taking a photo every minute.” Paliwal responded by pointing out that people are already “constantly taking mental photos.”
Others were more enthusiastic, with one user noting, “I’ve been searching for a device like this for years! A picture every minute should be enough if it archives, organizes, labels, and retrieves them.” Another user praised the concept, saying, “Love the idea. The design and name are perfect. Great work!”
Science
TEXAS: Meet Gopi Thotakura, Indian Who Will Soon Go To The Edge Of Outer Space
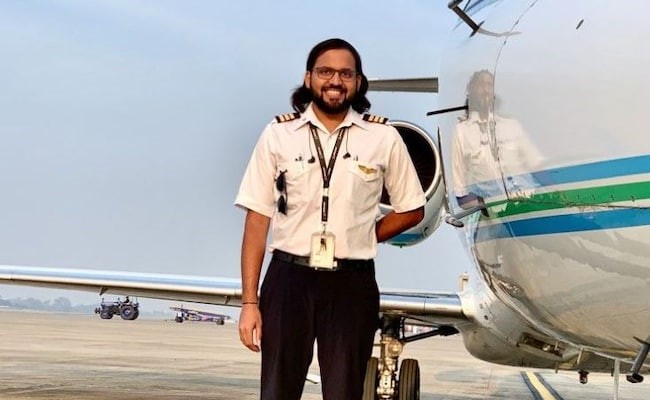

TEXAS: In an unprecedented leap towards the stars, pilot Gopichand Thotakura is set to become the first Indian to venture into space as a tourist. Selected as part of the elite crew for Blue Origin’s New Shephard-25 (NS-25) mission, Mr Thotakura will make a journey beyond the Earth’s atmosphere along with five other candidates.
Gopichand Thotakura, an entrepreneur and pilot, joins a distinguished lineup of 31 candidates who have flown beyond the Karman line, the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
A connoisseur of the skies since his youth, Mr Thotakura’s passion for flight saw him defy conventional norms, learning to pilot aircraft before mastering the art of driving. To further his passion, he graduated from Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University with a Bachelor of Science in Aeronautical Science.
Describing him, Blue Origins wrote, “Gopi is a pilot and aviator who learned how to fly before he could drive. Gopi pilots bush, aerobatic, and seaplanes, as well as gliders and hot air balloons, and has served as an international medical jet pilot. A lifelong traveler, his most recent adventure took him to the summit of Mt. Kilimanjaro.”
Born in Vijayawada, the 30-year-old currently runs Preserve Life Corp, a global center for holistic wellness and applied health located near Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport
Each member of the NS-25 mission will carry a postcard on behalf of Blue Origin’s foundation, Club for the Future, symbolizing the collective dreams and aspirations of young minds worldwide.
From an environmental standpoint, the NS-25 mission heralds a new era of sustainability in space exploration.
“Nearly 99% of New Shepard’s dry mass is reused, including the booster, capsule, engine, landing gear, and parachutes. New Shepard’s engine is fueled by highly efficient liquid oxygen and hydrogen. During flight, the only byproduct is water vapor with no carbon emissions,” Blue Origins said in their statement.
The launch date for the mission is yet to be announced.
The mission also includes former Air Force Captain Ed Dwight, who was selected by US President John F Kennedy in 1961 as the country’s first Black astronaut candidate but was never granted the opportunity to fly to space.
Blue Origin has carried out six crewed flights — some passengers were paying customers and others were guests — since July 2021, when CEO Jeff Bezos himself took part in the first.
The company is also developing a heavy rocket for commercial purposes called New Glenn, with the maiden flight planned for next year.
This rocket, which measures 98 meters (320 feet) high, is designed to carry payloads of as much as 45 metric tons into low Earth orbit.
Science
WASHINGTON: Who Is Aroh Barjatya, Indian-Origin Researcher Who Led Recent NASA Mission
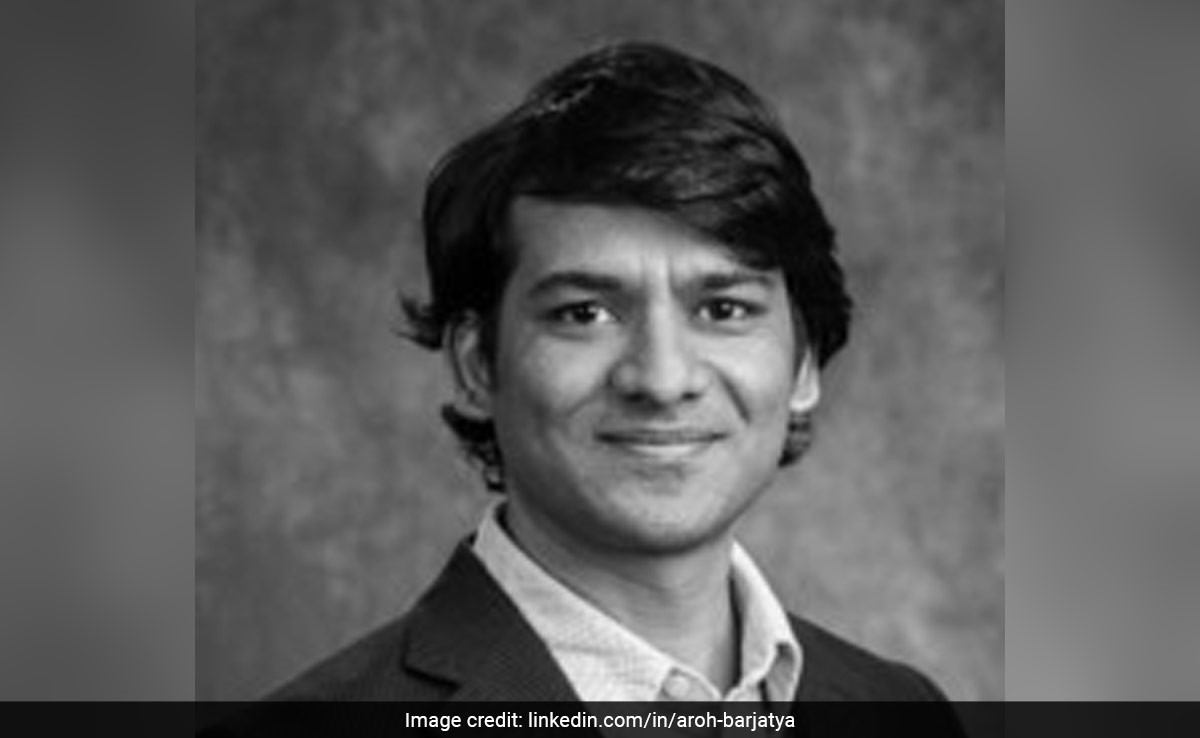

WASHINGTON: Aroh Barjatya, an India-born researcher, led NASA’s mission that launched sounding rockets during the recent total solar eclipse.
The US space agency launched three sounding rockets during the total solar eclipse on April 8 to study what happens to the Earth’s upper atmosphere when sunlight dims momentarily over a part of the planet.
Who Is Aroh Barjatya?
A professor of engineering physics, Aroh Barjatya directs the Space and Atmospheric Instrumentation Lab at the Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Florida.
Born to a chemical engineer, Ashok Kumar Barjatya, and his wife Rajeshwari, Aroh Barjatya went to schools across India, including in Patalganga near Mumbai, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Pilani, and Solapur.
He went on to get a degree in electronics engineering from Solapur’s Walchand Institute of Technology.
In 2021, he moved to the US for a master’s degree in electrical engineering at Utah State University. He later did his PhD in spacecraft instrumentation from the same university.
“In addition to leading an externally funded research enterprise, as a tenured faculty I have mentored and engaged young minds through inquiry-based learning tactics, created a new area of concentration within the Engineering Physics programme at ERAU… My mission is to advance the state of the art in space research and education and to inspire the next generation of space engineers and scientists,” he wrote on his LinkedIn profile.
-

 Diplomatic News1 year ago
Diplomatic News1 year agoSTOCKHOLM: Dr. Neena Malhotra appointed as the next Ambassador of India to the Kingdom of Sweden
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoMARYLAND: All About Pavan Davuluri, New Head Of Microsoft Windows
-
Opinions5 years ago
2020 will be remembered as time of the pandemic. The fallout will be felt for years
-

 Diplomatic News1 year ago
Diplomatic News1 year agoKINGSTON: Shri Subhash Prasad Gupta concurrently accredited as the next High Commissioner of India to St.Vincent and the Grenadines
-

 Politcs2 years ago
Politcs2 years agoLONDON: Indian-Origin Candidate On How He Plans To Win London Mayoral Polls
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoSINGAPORE CITY: Indian Wins Big In Singapore Company’s ‘Squid Game’ Survival Contest
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year agoWASHINGTON: Social Media Has Direct Impact On Mental Health- US Surgeon General To NDTV
-

 Science2 years ago
Science2 years agoWASHINGTON: Who Is Aroh Barjatya, Indian-Origin Researcher Who Led Recent NASA Mission














